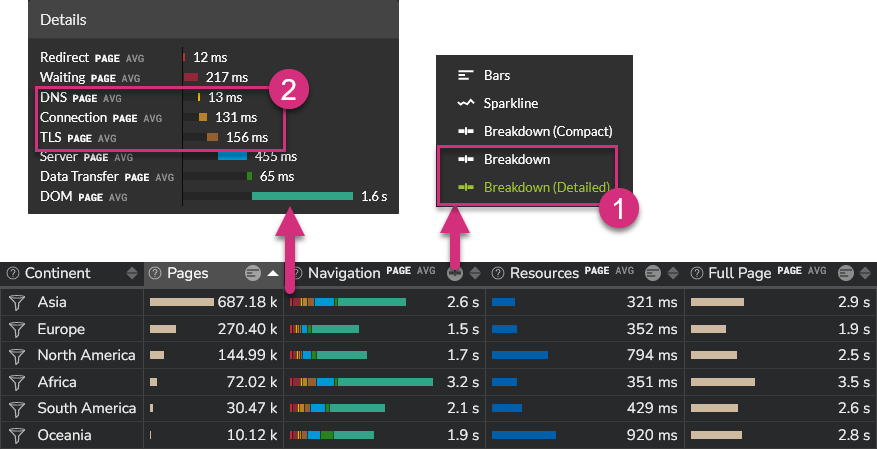
Network setup¶
Definition¶
The process of loading a web page can be split into the following main steps:
- The browser processes the request locally, checking for local cached data for example, before performing any network request
- If the resource is not available locally, it is requested on the network
- The server receives the request and processes it
- The requested data are transferred from the server to the browser through the network
- The web page is being rendered on the user's browser
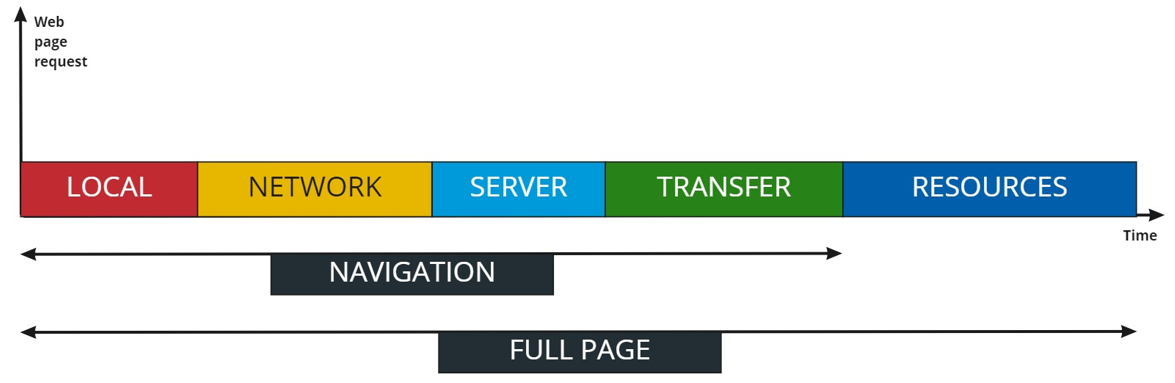
As shown on the W3C Time Navigation API view hereunder, the Network part includes the FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) resolution process as well as TCP/TLS session establishment, so that "Network Setup = DNS time + Connection Time + TLS time".
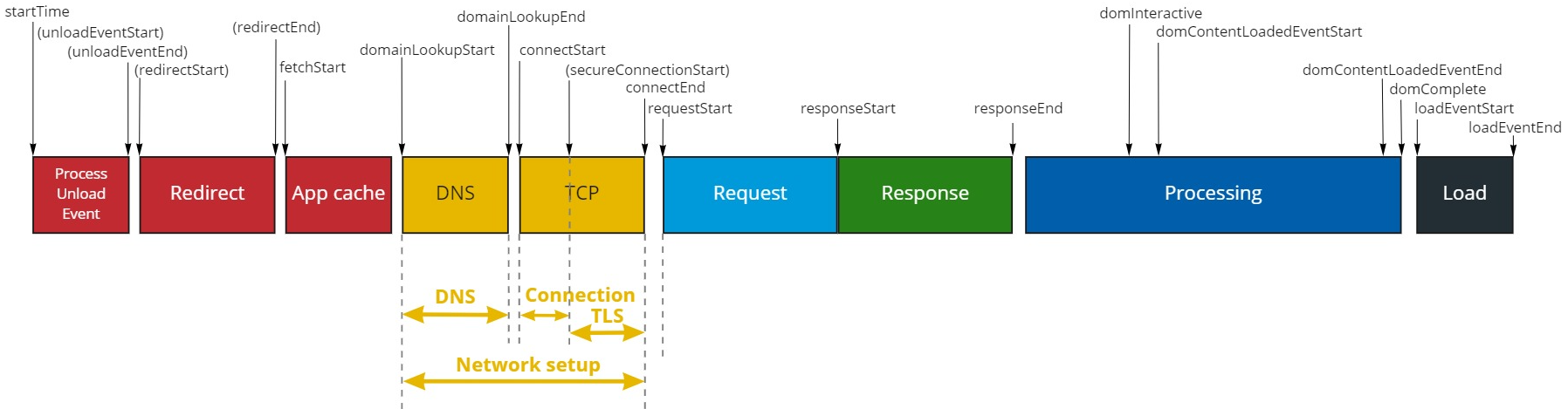
The Network value is provided at navigation level as well as at resources level. When you look at web page global performances in the "Scope Analysis" section, you see two main performance metrics :
- Navigation: time it takes to construct the web page structure
- Resources: time it takes to fetch all resources that compose the page
Mouseover on any Navigation breakdown bar to see more details, and more specifically here the value of the Network setup metric.
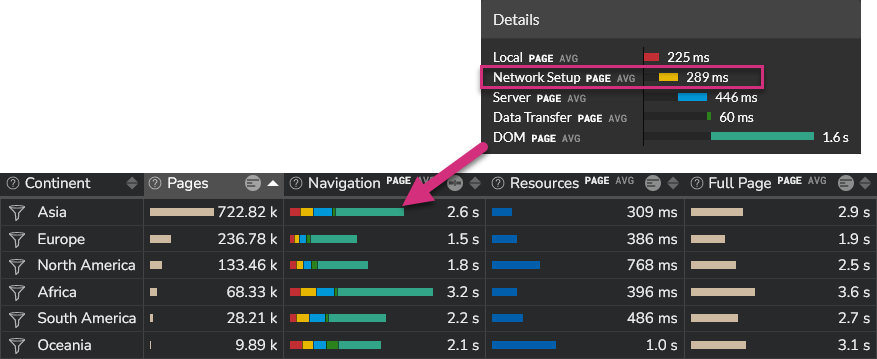
From this view, if you want to drill down to more detailed data, you can do it. From a "Network setup" measurement standpoint, you can directly see the "DNS", "Connection" and "TLS" details by activating the "breakdown (detailed)" view, as shown hereunder.